Exploratory data analysis II
Lecture 6
Warm-up
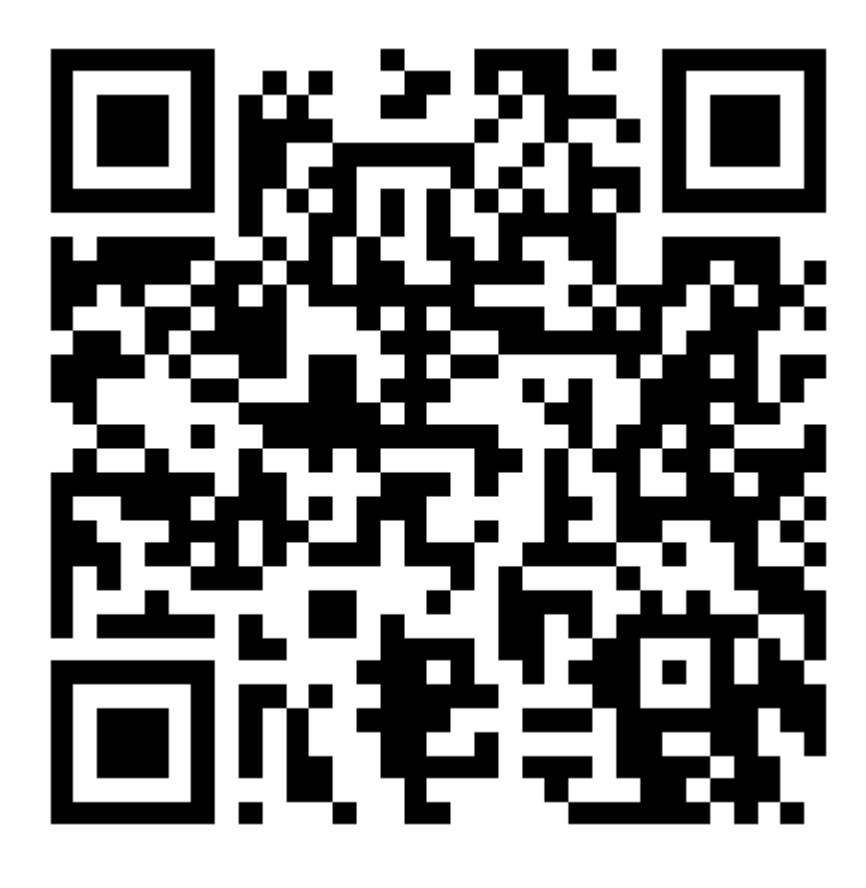
While you wait: Participate 📱💻
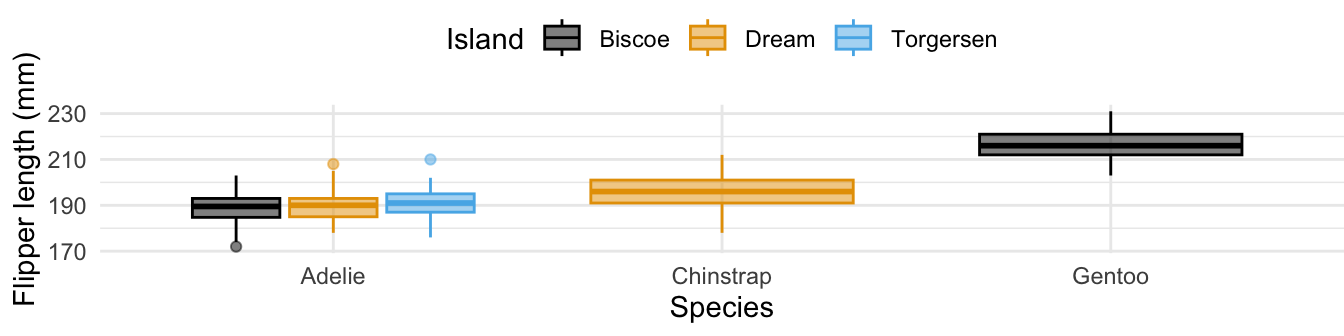
Which of the following is false about the following plot and the code that produced it?
Scan the QR code or go to app.wooclap.com/sta199. Log in with your Duke NetID.
- There are no Chinstrap or Gentoo penguins on Torgersen Island.
-
legend.position = "bottom"is set in thetheme()layer. - The same variable is mapped to both
colorandfill. -
group_by(species)is used to create the boxplots. - A Biscoe island penguin with a flipper length of 190 mm must be an Adélie.
Reminder: Code style and readability
Plots should include an informative title, axes and legends should have human-readable labels, and careful consideration should be given to aesthetic choices.
-
Code should follow the tidyverse style (style.tidyverse.org) Particularly,
- space before and line breaks after each
+when building aggplot - space before and line breaks after each
|>in a data transformation pipeline - code should be properly indented
- spaces around
=signs and spaces after commas
- space before and line breaks after each
All code should be visible in the PDF output, i.e., should not run off the page on the PDF. Long lines that run off the page should be split across multiple lines with line breaks. Tip: Haikus not novellas when writing code!
Whydowecareaboutthestyleandreadabilityofyourcode? \(\rightarrow\) Why do we care about the style and readability of your code?
Je voudrais un cafe \(\rightarrow\) Je voudrais un café
gerrymander
Packages
- For the data: usdata
From the AE
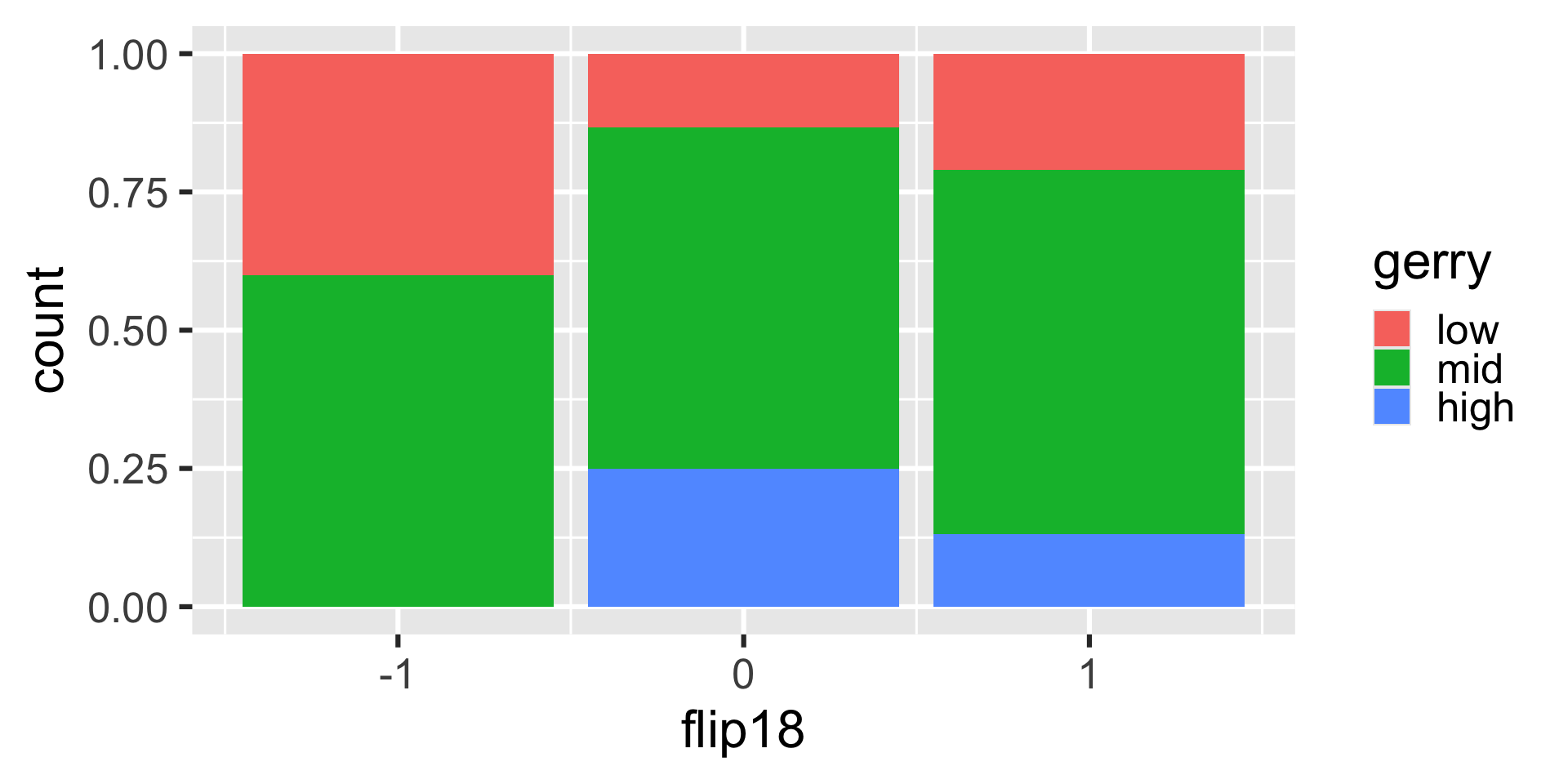
Is a Congressional District more likely to have high prevalence of gerrymandering if a Democrat flipped the seat in the 2018 election? (flip18 = 1: Democrat flipped the seat, 0: No flip, -1: Republican flipped the seat.)
ggplot(
gerrymander,
aes(x = flip18, fill = gerry)
) +
geom_bar(position = "fill") +
scale_fill_colorblind()
group_by(), summarize(), count()
Spot the difference
What does group_by() do?
gerrymander |>
count(flip18, gerry)# A tibble: 8 × 3
flip18 gerry n
<dbl> <fct> <int>
1 -1 low 2
2 -1 mid 3
3 0 low 52
4 0 mid 242
5 0 high 98
6 1 low 8
7 1 mid 25
8 1 high 5Let’s simplify!
What does group_by() do in the following pipeline?
group_by()
Group by converts a data frame to a grouped data frame, where subsequent operations are performed once per group
ungroup()removes grouping
# A tibble: 435 × 4
# Groups: state [50]
state district party16 party18
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 AK AK-AL R R
2 AL AL-01 R R
3 AL AL-02 R R
4 AL AL-03 R R
5 AL AL-04 R R
6 AL AL-05 R R
7 AL AL-06 R R
8 AL AL-07 D D
9 AR AR-01 R R
10 AR AR-02 R R
# ℹ 425 more rows# A tibble: 435 × 4
state district party16 party18
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 AK AK-AL R R
2 AL AL-01 R R
3 AL AL-02 R R
4 AL AL-03 R R
5 AL AL-04 R R
6 AL AL-05 R R
7 AL AL-06 R R
8 AL AL-07 D D
9 AR AR-01 R R
10 AR AR-02 R R
# ℹ 425 more rowsgroup_by() |> summarize()
A common pipeline is group_by() and then summarize() to calculate summary statistics for each group:
gerrymander |>
group_by(state) |>
summarize(
mean_trump16 = mean(trump16),
median_trump16 = median(trump16)
)# A tibble: 50 × 3
state mean_trump16 median_trump16
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 AK 52.8 52.8
2 AL 62.6 64.9
3 AR 60.9 63.0
4 AZ 46.9 47.7
5 CA 31.7 28.4
6 CO 43.6 41.3
7 CT 41.0 40.4
8 DE 41.9 41.9
9 FL 47.9 49.6
10 GA 51.3 56.6
# ℹ 40 more rowsgroup_by() |> summarize()
This pipeline can also be used to count number of observations for each group:
summarize()
... |>
summarize(
name_of_summary_statistic = summary_function(variable)
). . .
-
name_of_summary_statistic: Anything you want to call it!- Recommendation: Keep it short and evocative
-
summary_function():
Spot the difference
What’s the difference between the following two pipelines?
gerrymander |>
count(state)# A tibble: 50 × 2
state n
<chr> <int>
1 AK 1
2 AL 7
3 AR 4
4 AZ 9
5 CA 53
6 CO 7
7 CT 5
8 DE 1
9 FL 27
10 GA 14
# ℹ 40 more rowscount()
Count the number of observations in each level of variable(s)
Place the counts in a variable called
n
Participate 📱💻
How would you write the following pipeline with count() instead?
# A tibble: 50 × 2
state n
<chr> <int>
1 CA 53
2 TX 36
3 FL 27
4 NY 27
5 IL 18
6 PA 18
7 OH 16
8 GA 14
9 MI 14
10 NC 13
# ℹ 40 more rowsgerrymander |> arrange(state) |> count()gerrymander |> count(state) |> arrange(desc(n))gerrymander |> count(state) |> sort(n)gerrymander |> count(state, sort = TRUE)
Scan the QR code or go to app.wooclap.com/sta199. Log in with your Duke NetID.
mutate()
Flip the question
Is a Congressional District more likely to have high prevalence of gerrymandering if a Democrat flipped the seat in the 2018 election?
vs.
Is a Congressional District more likely to be flipped to a Democratic seat if it has high or low prevalence of gerrymandering?
What’s going on?
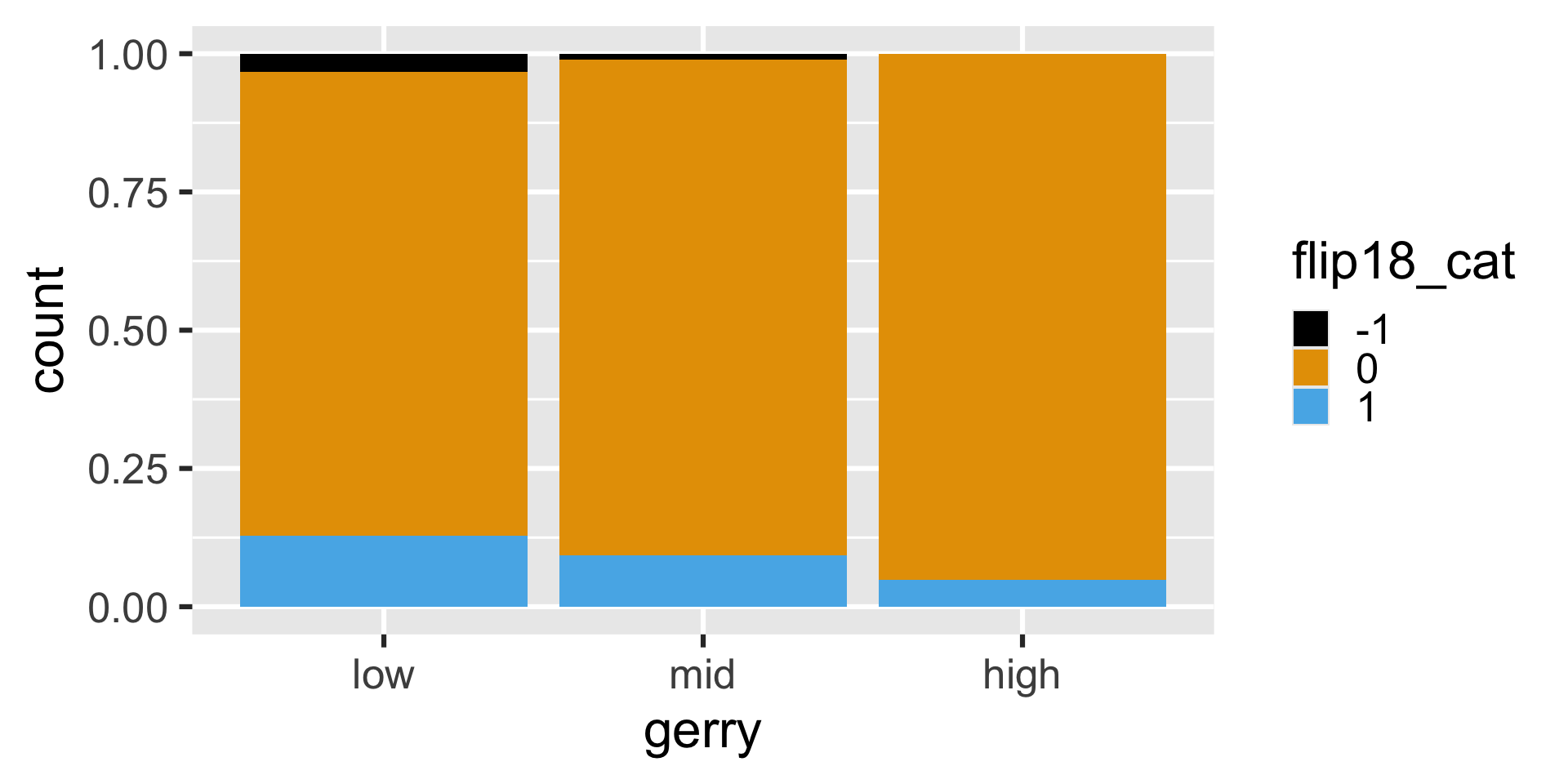
The following code should produce a visualization that answers the question “Is a Congressional District more likely to be flipped to a Democratic seat if it has high or low prevalence of gerrymandering?” However, it produces a warning and an unexpected plot. What’s going on?
Warning: The following aesthetics were dropped during statistical
transformation: fill.
ℹ This can happen when ggplot fails to infer the correct grouping
structure in the data.
ℹ Did you forget to specify a `group` aesthetic or to convert a
numerical variable into a factor?Another glimpse at gerrymander
glimpse(gerrymander)Rows: 435
Columns: 12
$ district <chr> "AK-AL", "AL-01", "AL-02", "AL-03", "AL-04", "AL-…
$ last_name <chr> "Young", "Byrne", "Roby", "Rogers", "Aderholt", "…
$ first_name <chr> "Don", "Bradley", "Martha", "Mike D.", "Rob", "Mo…
$ party16 <chr> "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "D", "R", "R",…
$ clinton16 <dbl> 37.6, 34.1, 33.0, 32.3, 17.4, 31.3, 26.1, 69.8, 3…
$ trump16 <dbl> 52.8, 63.5, 64.9, 65.3, 80.4, 64.7, 70.8, 28.6, 6…
$ dem16 <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0…
$ state <chr> "AK", "AL", "AL", "AL", "AL", "AL", "AL", "AL", "…
$ party18 <chr> "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "D", "R", "R",…
$ dem18 <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0…
$ flip18 <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0…
$ gerry <fct> mid, high, high, high, high, high, high, high, mi…mutate()
We want to use
flip18as a categorical variableBut it’s stored as a numeric
So we need to change its type first, before we can use it as a categorical variable
The
mutate()function transforms (mutates) a data frame by creating a new column or updating an existing one
mutate() in action
You can create a new variable with mutate():
gerrymander |>
mutate(flip18_cat = as.factor(flip18)) |>
relocate(district, flip18, flip18_cat) # relocate to the beginning for easier viewing# A tibble: 435 × 13
district flip18 flip18_cat last_name first_name party16 clinton16
<chr> <dbl> <fct> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 AK-AL 0 0 Young Don R 37.6
2 AL-01 0 0 Byrne Bradley R 34.1
3 AL-02 0 0 Roby Martha R 33
4 AL-03 0 0 Rogers Mike D. R 32.3
5 AL-04 0 0 Aderholt Rob R 17.4
6 AL-05 0 0 Brooks Mo R 31.3
7 AL-06 0 0 Palmer Gary R 26.1
8 AL-07 0 0 Sewell Terri D 69.8
9 AR-01 0 0 Crawford Rick R 30.2
10 AR-02 0 0 Hill French R 41.7
# ℹ 425 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: trump16 <dbl>, dem16 <dbl>, state <chr>,
# party18 <chr>, dem18 <dbl>, gerry <fct>Revisit the plot
Is a Congressional District more likely to be flipped to a Democratic seat if it has high or low prevalence of gerrymandering?
mutate() and overwrite
You can overwrite an existing variable with mutate():
mutate() and if_else()
Use mutate() with if_else() to recode with an either/or logic:
If
party16is “D”, recode it as “Democrat”, otherwise recode it as “Republican”.
gerrymander |>
mutate(party16_expanded = if_else(party16 == "D", "Democrat", "Republican")) |>
select(district, party16, party16_expanded)# A tibble: 435 × 3
district party16 party16_expanded
<chr> <chr> <chr>
1 AK-AL R Republican
2 AL-01 R Republican
3 AL-02 R Republican
4 AL-03 R Republican
5 AL-04 R Republican
6 AL-05 R Republican
7 AL-06 R Republican
8 AL-07 D Democrat
9 AR-01 R Republican
10 AR-02 R Republican
# ℹ 425 more rows
mutate() and case_when()
Use mutate() with case_when() to recode with a more complex logic:
If
flip18is 1, recode it as “Democrat flipped”, ifflip18is 0, recode it as “No flip”, and ifflip18is -1, recode it as “Republican flipped”.
gerrymander |>
mutate(
flip18_expanded = case_when(
flip18 == 1 ~ "Democrat flipped",
flip18 == 0 ~ "No flip",
flip18 == -1 ~ "Republican flipped"
)
) |>
select(district, flip18, flip18_expanded) |>
group_by(flip18) |> # group by flip type
slice_head(n = 1) # show top row per group# A tibble: 3 × 3
# Groups: flip18 [3]
district flip18 flip18_expanded
<chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 MN-01 -1 Republican flipped
2 AK-AL 0 No flip
3 AZ-02 1 Democrat flipped
mutate() and store
If you want to keep your changes, you need to store the data frame after mutate():
gerrymander |>
mutate(
p16 = if_else(party16 == "D", "Dem", "Rep")
) |>
select(district, p16) |>
slice_head(n = 3) # show top 3 rows# A tibble: 3 × 2
district p16
<chr> <chr>
1 AK-AL Rep
2 AL-01 Rep
3 AL-02 Rep gerrymander |>
select(district, p16)Error in `select()`:
! Can't select columns that don't exist.
✖ Column `p16` doesn't exist.gerrymander <- gerrymander |>
mutate(
p16 = if_else(party16 == "D", "Dem", "Rep")
) |>
select(district, p16)
gerrymander |>
select(district, p16) |>
slice_head(n = 3) # show top 3 rows# A tibble: 3 × 2
district p16
<chr> <chr>
1 AK-AL Rep
2 AL-01 Rep
3 AL-02 Rep Application exercise
ae-04-gerrymander-explore-II
Go to your ae project in RStudio.
If you haven’t yet done so, make sure all of your changes up to this point are committed and pushed, i.e., there’s nothing left in your Git pane.
If you haven’t yet done so, click Pull to get today’s application exercise file: ae-04-gerrymander-explore-II.qmd.
Work through the application exercise in class, and render, commit, and push your edits by the end of class.
Recap: aesthetic mappings
Local aesthetic mappings for a given
geomGlobal aesthetic mappings for all
geoms