── Attaching core tidyverse packages ────────────── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.5
✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.1
✔ ggplot2 3.5.2 ✔ tibble 3.3.0.9004
✔ lubridate 1.9.4 ✔ tidyr 1.3.1
✔ purrr 1.1.0
── Conflicts ──────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errorsData types and classes
Lecture 9
Duke University
STA 199 - Fall 2025
September 23, 2025
Warm-up
While you wait: Participate 📱💻
Fill in the blanks:
I’m a _____ (first-year, sophomore, junior, senior)
and on Tuesdays I have _____ class(es).

Scan the QR code or go to app.wooclap.com/sta199. Log in with your Duke NetID.
Announcements
Survey: Confidence in STEM courses at Duke

Exam 1:
- In class on Thu, Oct 2
- Take home Thu, Oct 2 after class until Sat, Oct 4 at noon
- Covers lectures 1-10, labs 1-4, and homeworks 1-3
- Practice exam to be posted on Friday, exam review on Tue, Sep 30
Recap: The tidyverse package
When you load the tidyverse package, you get access to a suite of packages that work well together for data manipulation and visualization:
You never need to load one of these packages individually after you load the tidyverse, e.g.,
Recap: Loading packages
- You only need to load a package once per R session or Quarto document.
- It’s good practice to load all the packages you need at the start of your document, that’s why the templates I give you usually has a
load-packagescode cell at the top.
- You never need to load these packages again further down in the same document.
- If you need a new package further down in the document, go back and add it to the
load-packagescode cell.
Recap: Pipes

This is not a pipe.
Recap: Pipes

This is not our pipe [operator].
Recap: Pipes

This is our a pipe [operator].
Data types
How many classes do you have on Tuesdays?
Variable types
What type of variable is tue_classes?
Let’s (attempt to) clean it up…
survey <- survey |>
mutate(
tue_classes = case_when(
tue_classes == "one" ~ "1",
tue_classes == "two" ~ "2",
tue_classes == "Two" ~ "2",
.default = tue_classes
),
tue_classes = as.numeric(tue_classes),
year = case_when(
year == "Sophmore" ~ "Sophomore",
year == "Freshman" ~ "First-year",
.default = year
)
) |>
filter(year != "29.32%")
survey# A tibble: 85 × 2
year tue_classes
<chr> <dbl>
1 Senior 3
2 Sophomore 4
3 Sophomore 3
4 Junior 4
5 Sophomore 2
6 First-year 2
7 Junior 2
8 Sophomore 3
9 First-year 2
10 Senior 3
# ℹ 75 more rowsData types
Data types in R
- logical
- double
- integer
- character
- and some more, but we won’t be focusing on those
Logical & character
Double & integer
Concatenation
Vectors can be constructed using the c() function.
- Numeric vector:
Converting between types
with intention…
Converting between types
with intention…
Converting between types
without intention…
R will happily convert between various types without complaint when different types of data are concatenated in a vector, and that’s not always a great thing!
Converting between types
without intention…
Participate 📱💻
What is the output of typeof(c(1.2, 3L))?
"character""double""integer""logical"

Scan the QR code or go to app.wooclap.com/sta199. Log in with your Duke NetID.
Explicit vs. implicit coercion
Explicit coercion:
When you call a function like as.logical(), as.numeric(), as.integer(), as.double(), or as.character().
Implicit coercion:
Happens when you use a vector in a specific context that expects a certain type of vector.
Data classes
Data classes
- Vectors are like Lego building blocks
- We stick them together to build more complicated constructs, e.g. representations of data
- The class attribute relates to the S3 class of an object which determines its behaviour
- You don’t need to worry about what S3 classes really mean, but you can read more about it here if you’re curious
- Examples: factors, dates, and data frames
Factors
R uses factors to handle categorical variables, variables that have a fixed and known set of possible values
More on factors
We can think of factors like character (level labels) and an integer (level numbers) glued together
Dates
More on dates
We can think of dates like an integer (the number of days since the origin, 1 Jan 1970) and an integer (the origin) glued together
Data frames
We can think of data frames like like vectors of equal length glued together
Lists
Lists are a generic vector container; vectors of any type can go in them
Lists and data frames
- A data frame is a special list containing vectors of equal length
- When we use the
pull()function, we extract a vector from the data frame
Working with factors
Read data in as character strings
But coerce when plotting
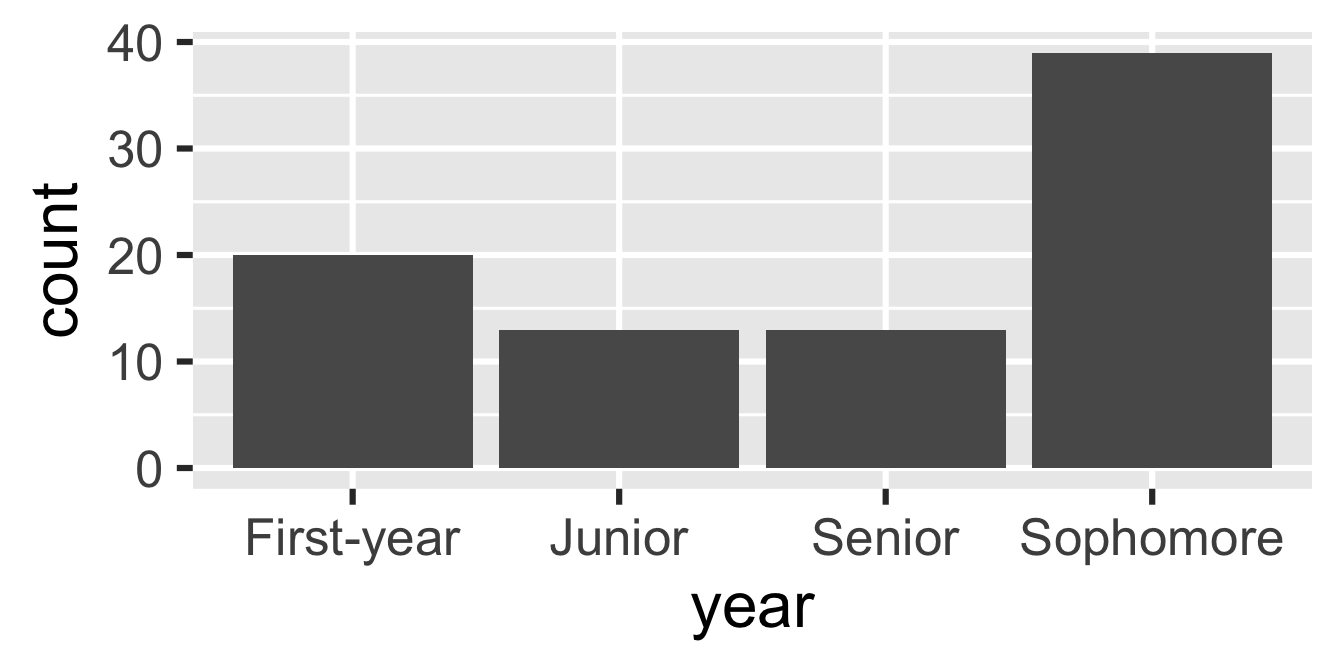
Use forcats to reorder levels
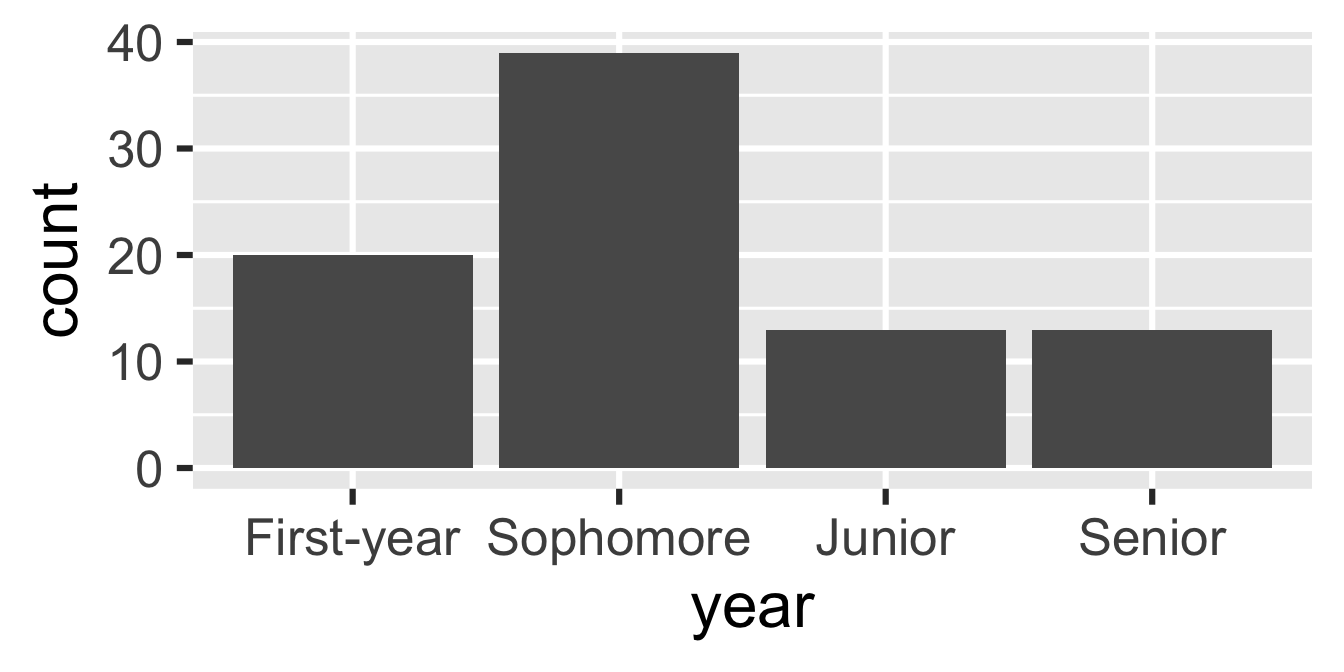
A peek into forcats
Reordering levels by:
fct_relevel(): handfct_infreq(): frequencyfct_reorder(): sorting along another variablefct_rev(): reversing
…
Changing level values by:
fct_lump(): lumping uncommon levels together into “other”fct_other(): manually replacing some levels with “other”
…
Application exercise
ae-08-durham-climate-factors
Go to your ae project in RStudio.
If you haven’t yet done so, make sure all of your changes up to this point are committed and pushed, i.e., there’s nothing left in your Git pane.
If you haven’t yet done so, click Pull to get today’s application exercise file: ae-08-durham-climate-factors.qmd.
Work through the application exercise in class, and render, commit, and push your edits by the end of class.
